quantitative sampling plan|quantitative sampling meaning : distributors Sampling in quantitative research is a critical component that involves selecting a representative subset of individuals or cases from a larger population and often employs sampling techniques . webNo Clube Tauste, você pode aproveitar ofertas especiais e descontos em suas compras na Rede Tauste Supermercados. Basta se cadastrar no Clube, informar o CPF na hora da compra e participar de campanhas .
{plog:ftitle_list}
O Vick Vaporub deve ser usado para inalação ou aplicação sobre a pele, sendo que a posologia normalmente recomendada para adultos e crianças com mais de 2 anos inclui: Ver mais
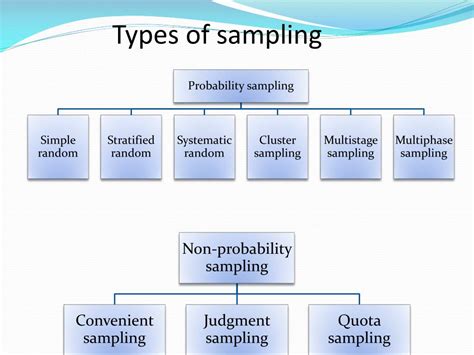
Sampling in quantitative research is a critical component that involves selecting a representative subset of individuals or cases from a larger population and often employs sampling techniques .Part I: Sampling, Data Collection, & Analysis in Quantitative Research. In this module, we will focus on how quantitative research collects and analyzes data, as well as methods for .
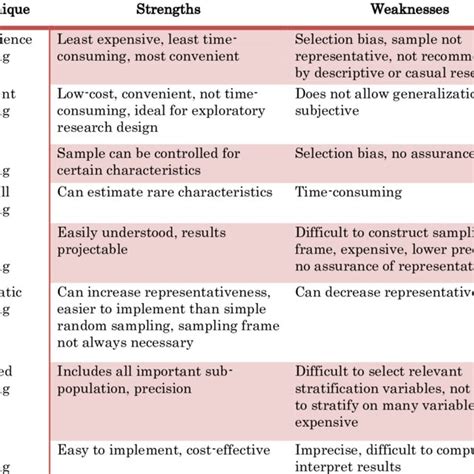
Describe how you will recruit your participants and how your plan makes sense with the sampling approach you identified. Examine one of the empirical articles from your . Specifically, the following section discusses the importance of sampling techniques, the types of sampling techniques along with advantages and disadvantages, and . Sampling methods in psychology refer to strategies used to select a subset of individuals (a sample) from a larger population, to study and draw inferences about the entire population. Common methods include . This article reviews probability and non-probability sampling methods, lists and defines specific sampling techniques, and provides pros and cons for consideration. In .
types of sampling in quantitative
types of quantitative sampling methods
In this paper, the basic elements related to the selection of participants for a health research are discussed. Sample representativeness, sample frame, types of sampling, as well as the .
Abstract In quantitative research, collecting data from an entire population of a study is impractical in many instances. It squanders resources like time and money which can be minimized by .The following will present information on the elements of sampling plans in both qualitative and quantitative research, a part of a work unit in the Track 2 Dissertation Research Seminar courseroom. Objectives. This document will discuss the elements of the sampling plan, which include the: Sampling strategy. Sampling design. Size of the sample.
quantitative sampling techniques pdf
Sampling methods in psychology refer to strategies used to select a subset of individuals (a sample) from a larger population, to study and draw inferences about the entire population. Common methods include .Chapter Outline. The sampling process (25 minute read); Sampling approaches for quantitative research (15 minute read); Sample quality (24 minute read); Content warning: examples contain references to addiction to technology, . The sampling technique in quantitative research comes from its ability to draw small units of the population (i.e., sample size) and generalize it to the population (Seddon & Scheepers, 2012).In a study, specifically in behavioural research where the number of population elements is too large, collecting data from every element of a population is unreal. Probability sampling. Unlike nonprobability sampling, probability sampling refers to sampling techniques for which a person’s likelihood of being selected from the sampling frame is known. You might ask yourself why we should care about a potential participant’s likelihood of being selected for the researcher’s sample.
quantitative sampling technique
Sampling in quantitative research projects is done because it is not feasible to study the whole population, and researchers hope to take what we learn about a small group of people (your sample) and apply it to a larger population. . Building on the step-by-step sampling plan from the exercises in section 10.1: Quantitative research methods. You can use quantitative research methods for descriptive, correlational or experimental research. In descriptive research, you simply seek an overall summary of your study variables.; In correlational research, you investigate relationships between your study variables.; In experimental research, you systematically examine whether . Oversimplified info on sampling methods. Probabilistic of the sampling and sampling of samples by chance does rest solely on the random methods. Factors such as the random visits or presentation of the potential participants at clinics or sites could be sufficiently random in nature and should be used for the sake of efficiency and feasibility. PDF | Broadly speaking, in quantitative research, two types of samples are used. The first, and most common, is the representative sample. . Sampling in quantitative research. July 2008 .
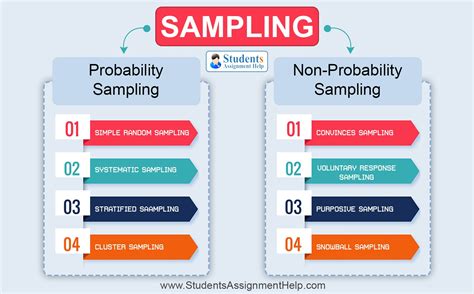
Probability sampling is a sampling method that involves randomly selecting a sample, or a part of the population that you want to research. FAQ About us . . Non-probability sampling designs are used in both quantitative and qualitative research when the number of units in the population is either unknown or impossible to individually identify .If your professor plans to generalize their results to all college students, then they will have to make an argument that their sampling frame (undergraduates at your school) is representative of the population (all undergraduate college students). Types of probability samples. There are a variety of probability samples that researchers may use.If your professor plans to generalize her results to all college students, she will have to make an argument that her sampling frame (undergraduates at your school) is representative of the population (all undergraduate college students). Types of probability samples. There are a variety of probability samples that researchers may use.
You might remember studying sampling in a quantitative research course. Sampling is important here too, but it works a bit differently. Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research involves nonprobability sampling. This chapter explains why this is so and what qualities instead make a good sample for qualitative research. When to use simple random sampling. Simple random sampling is used to make statistical inferences about a population. It helps ensure high internal validity: randomization is the best method to reduce the impact of potential confounding variables.. In addition, with a large enough sample size, a simple random sample has high external validity: it represents the .
quantitative sampling procedure
Knowledge of sampling methods is essential to design quality research. Critical questions are provided to help researchers choose a sampling method. This article reviews probability and non-probability sampling methods, lists and defines specific sampling techniques, and provides pros and cons for consideration.
test elemento genshin impact
The sampling process (25 minute read time); Sampling approaches for quantitative research (15 minute read time); Sample quality (24 minute read time); Content warning: examples contain references to addiction to . When to use systematic sampling. Systematic sampling is a method that imitates many of the randomization benefits of simple random sampling, but is slightly easier to conduct.. You can use systematic sampling with a list of the entire population, like you would in simple random sampling.However, unlike with simple random sampling, you can also use this .
Sampling plan is detailed outline of measurements to be taken: A sampling plan is a detailed outline of which measurements will be taken at what times, on which material, in what manner, and by whom. Sampling plans should be designed in such a way that the resulting data will contain a representative sample of the parameters of interest and .
test engineering and management journal impact factor
• Before collecting either qualitative or quantitative data, you should determine the adequate sample size. • Qualitative data collection is less dependent on large sample sizes and tends to involve nonrandom sampling types. • Quantitative data collection requires larger sample sizes and tends to involve random sampling types.Sampling can be divided in a number of different ways. At a basic level, with the exception of total population sampling you will often see the divide between random sampling of a representative population and non-random sampling. Clearly, for many more quantitative-minded researchers, non-random sampling is the second-choice approach as it createsThat is the first step in formulating a quantitative research plan. Formulate a hypothesis. This step is key. Researchers need to know exactly what they are testing so that testing the hypothesis can be achieved through specific statistical analyses. . Sampling. The researcher needs to determine a subset of the population that is to be .
A random sampling is the easiest way to satisfy this requirement [Cohen, R. D. J. Chem. Educ. 1991, 68, 902–903]. Despite its apparent simplicity, a truly random sample is difficult to collect. Haphazard sampling, in which samples are collected without a sampling plan, is not random and may reflect an analyst’s unintentional biases.
E.1.6 Perform the Sampling Plan, 312 E.1.7 Evaluate Sample Results, 312 E.2 op‐or‐GSt o Sampling, 313 E.2.1 Acceptable Deviation Rate, 313 E.2.2 Sample Size, 314 E.2.3 Evaluation, 316 E.3 One Hundred Percent Inspection, 316 E.4 Application: An Attribute Sampling Plan, 317 Referenc es, 318 Statistical Sampling PlansThe findings in this paper are based on the results of our drug homogeneity studies and particle size investigations. Using that information, a general sampling plan (depicted in the form of a flow-chart) was devised that could be applied to the quantitative instrumental analysis of the most common illicit drugs: namely heroin, cocaine, amphetamine, cannabis resin, MDMA .determining sample size and then create a sampling plan for your evaluation. There are two types of data you might collect: quantitative data and qualitative data. Quantitative data are numeric and answer, “how much” and “to what extent” questions. Qualitative data are non-numeric and answer, “why” and “how” questions. This module focuses on the discussion of your research design and plan, population to consider, sampling technique, research instruments, and appropriate statistical treatments to be employed. At end of this learning module learners are expected to understand the . Quantitative research is more systematic and controlled than qualitative. However,
Developing a Quantitative Data Analysis Plan 2013 Page 4 of 12 Methods The methods section is the main component of the data analysis plan. The methods should include details on: Data sources Study population: include a .
test for fecal impaction
test for impact not variation
web1 dia atrás · Bônus Pixbet e Código promocional Pixbet Cadastro Saques Março 2024. A empresas Pixbet é confiavel ou se trata de uma fraude? Como funciona e o que .
quantitative sampling plan|quantitative sampling meaning